Anatomy 結構
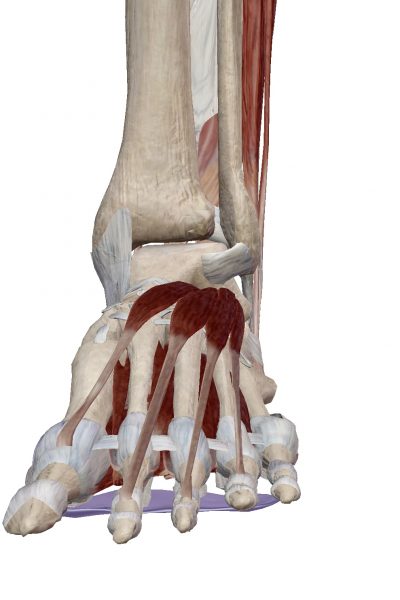
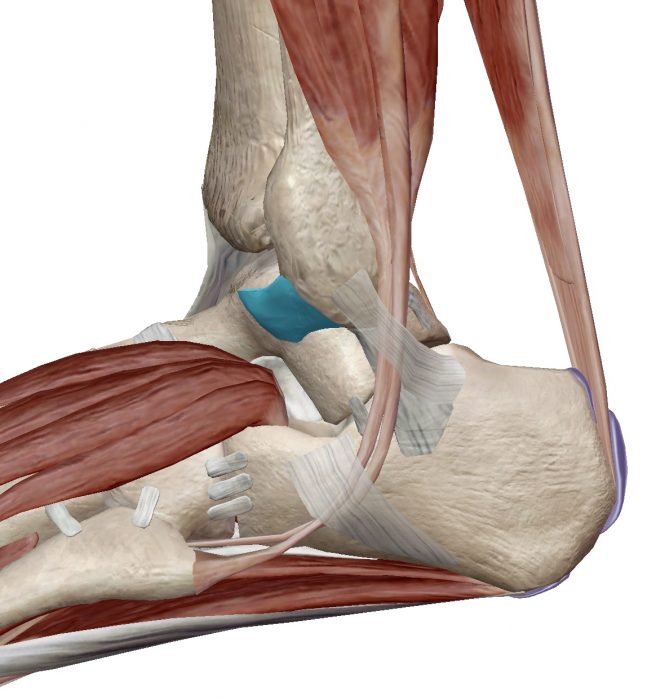
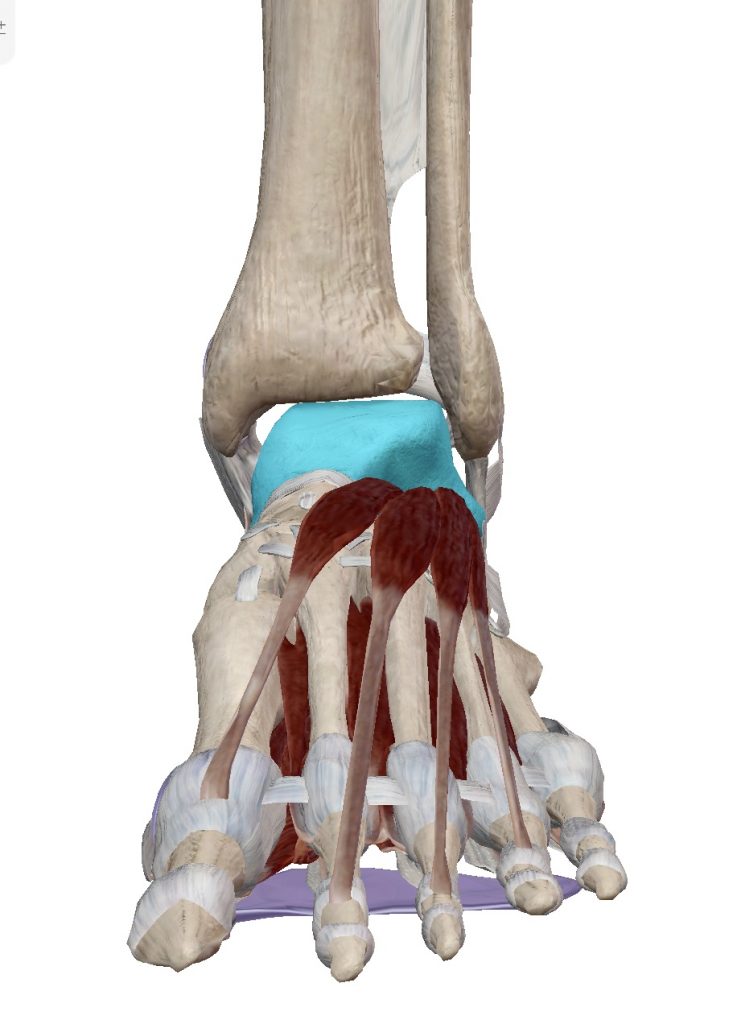
Ankle is a joint made of 4 bones, Tibia and fibula (the shin bone), talus (the ankle bone) and calcaneum (the heel bone). This ankle joint proper allow good planar motion of ankle up and down (called ankle dorsiflexion when up and plantarflexion when down). It also allows some rotation of the heel to accomodate slanting ground. Therefore, in theory, the ankle should involve the midfoot, which has 5 more bones, cuboid, navicula and 3 cuneiforms.
The talus is sitting in a mortise like structure formed by the two shin bones. Apart from the bony contour which offers good stability, it has strong ligaments on either side. The outer ligaments are frequently involved in sprain injury. When these ligament is torn, there will be abnormal translation and rotation. This sense of instability is particularly obvious when one descending on stairs especially with pivoting, i.e. on platform between two flights of stairs.
Pathology 毛病
Disease 病變
The followings are common pathologies in ankle
以下是常見足踝病變
- Anterior TaloFibular Ligament (ATFL) tear
- Ankle fracture
- Osteochondral lesion at talus dome
- Talus neck fracture
- Calcaneal fracture
- Loose body
- Posterior impingement
- hindfoot valgus
- Structural flatfoot
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- 前距腓韌帶(ATFL)撕裂
- 腳踝骨折
- 距骨骨軟骨病變
- 距骨頸骨折
- 跟骨骨折
- 關節碎骨
- 踝後受壓
- 後足外翻
- 結構性扁平足
- 足腕管綜合症
Investigation 評估
MRI is required to review soft tissue status. X-ray would be needed for bony pathology. Nerve conduction study might be indicated for possible nerve palsy.
磁力共震片能夠提供軟組織情況。骨頭問題,例如骨折,就會需要照X光。神經線問題可以電神經測試得知情況。
Management 治療
Conservative treatments are indicated for majority of cases. They included,
- Physiotherapy
- Chiropractor
- TCM practitioner
- Prescribed Exercise
- Medication
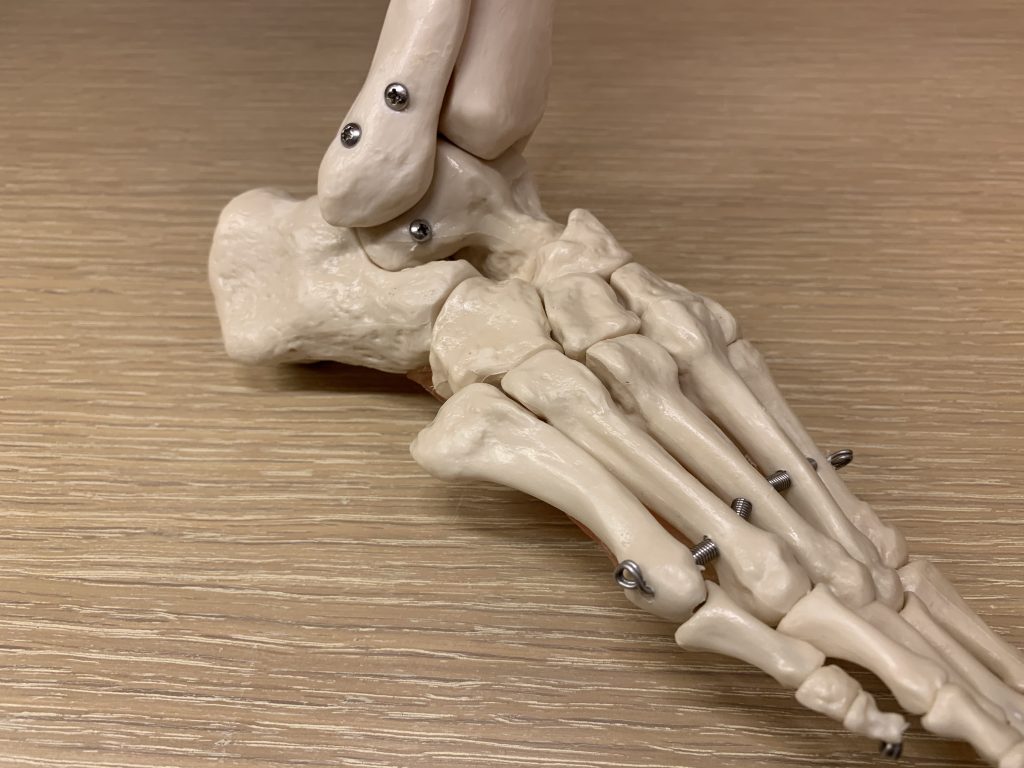
For cases failed conservative treatments, or when the injury is unstable, then surgical intervention would be indicated.
For patients with witnessed deterioration, surgical intervention might be advocated.
絕大多數病人只需採取保守治療。他們包括
- 物理治療
- 脊醫
- 中醫
- 處方運動
- 藥物(口服及外敷)
對於保守治療無效的病例,或受傷位置不穩定,醫生會改為介入治療,例如打針甚至手術。
對於持續惡化的患者,醫生往往會建議手術,以保肢體功能。
Common Interventions include
- Injection of steroid
- Injection of PRP
- Injection of hyaluronic acid
- casting
- Arthroscopic microfracture
- Arthroscopic loose body removal
- Arthroscopy assisted ligament repair
- Ligament reconstruction (ATFL reconstruction)
- Calcaneum osteotomy
- Surgical reduction and plating
- Osteochondral autograft
- Joint fusion
Reference
- Badekas T, Takvorian M, Souras N.
Treatment principles for osteochondral lesions in foot and ankle.
Int Orthop. 2013 Sep;37(9):1697-706. doi: 10.1007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23982639/

